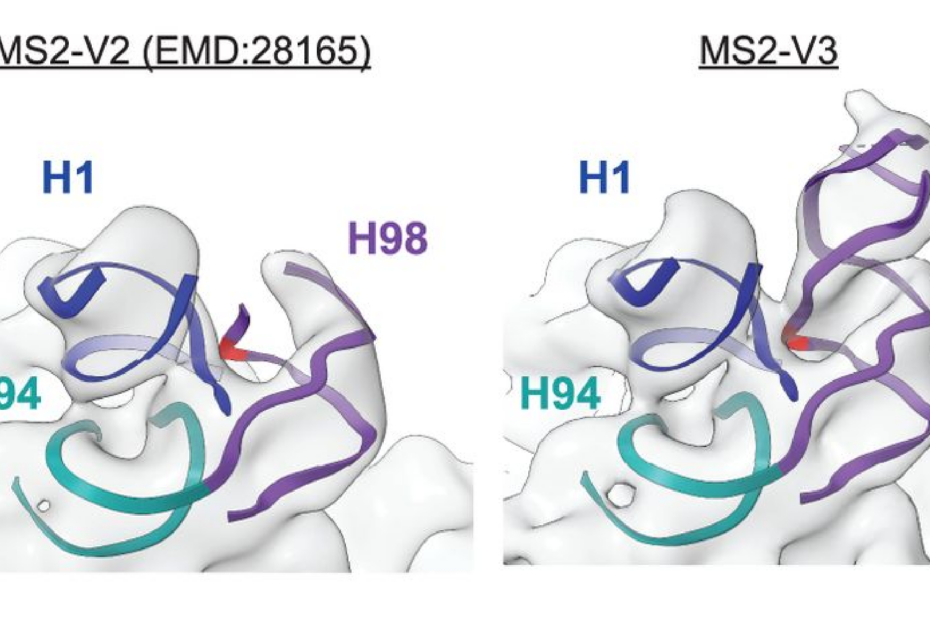
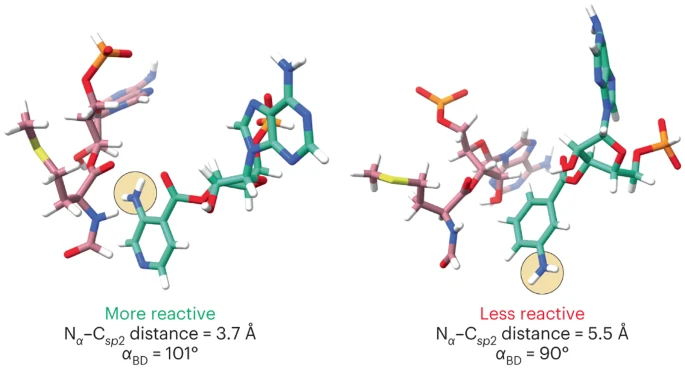
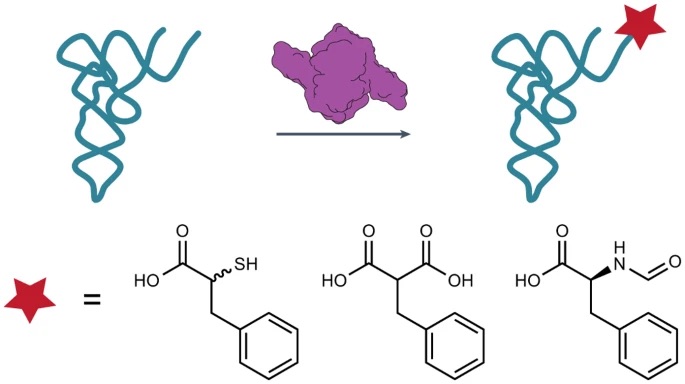
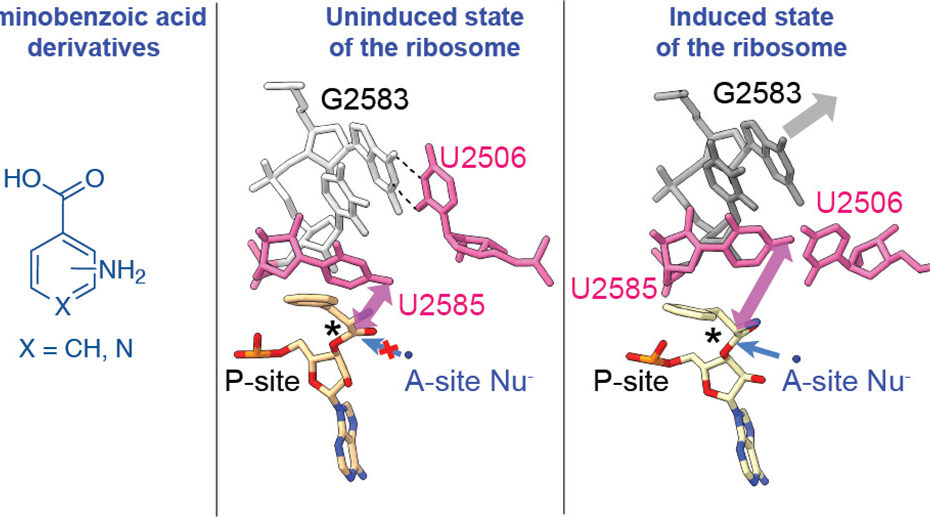
RNA language models predict mutations that improve RNA function (Nat Commun, 2024)
C-GEM published a new paper in Nature Communications in collaboration with the Innovative Genomics Institute. Our researchers developed an RNA language model to predict mutations that could lead to improved structural stability. This model was used to predict mutations that could lead to improved thermostability… Read More »RNA language models predict mutations that improve RNA function (Nat Commun, 2024)