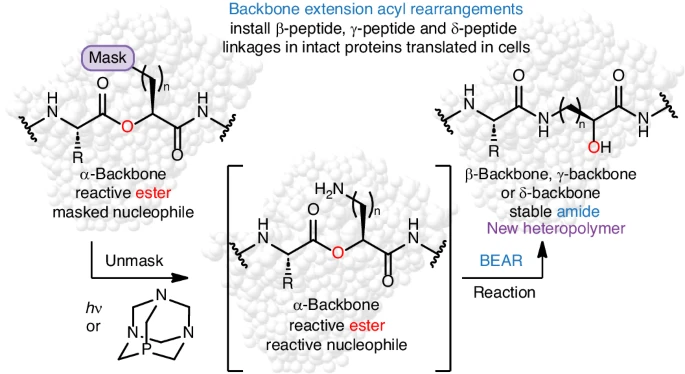
Researchers at the NSF Center for Genetically Encoded Materials (C-GEM) developed a novel and versatile chemo-ribosomal strategy to generate isolable quantities of protein-derived biopolymers containing site-specific backbone modifications. This strategy relies on an intramolecular backbone-extension acyl rearrangement (BEAR) reaction that post-translationally and site-specifically rearranges the backbone to introduce a new functional unit, in this case a β2-, ɣ-, or δ-linkage.
This work involved contributions from the Chatterjee lab, Francis lab, Miller lab, and Schepartz lab.