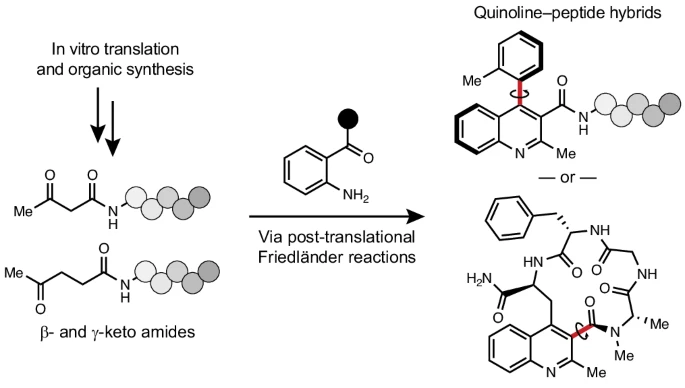
Most scientists have a complex love/hate relationship with peptides, especially in the field of drug discovery. Peptides are encodable, for sure, but they are also structurally featureless and often display exceptionally poor bioavailability and cell permeability. In this work, C-GEM researchers developed chemistry with the potential to solve both of these problems. They report methods to add complex heterocycles to the N-termini of encoded peptides, and others that embed the heterocycle directly within the macrocyclic peptide backbone, in certain cases forming pairs of separable atropisomers. Thus the chemistry reported can be employed to generate molecules endowed with both topological constraints (macrocyclization) as well as rotational constraints (atropisomerism). The reactions described are fully compatible with the native translation machinery, enabling their use in trillion-member peptide libraries for early drug-discovery efforts.
This work involved contributions from the Gonen lab, Schepartz lab, and Miller lab.