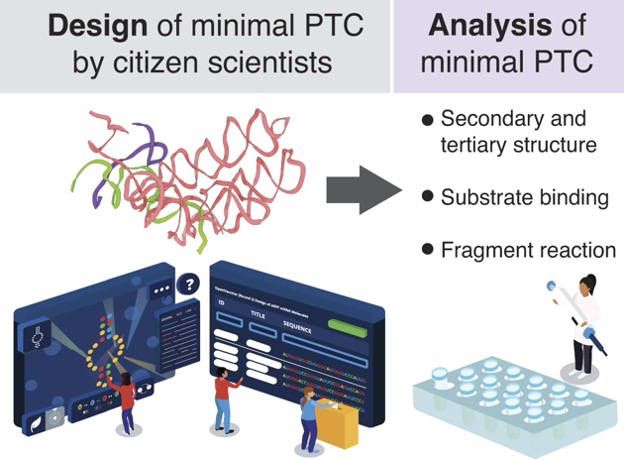
The ribosome is a ribonucleoprotein complex found in all domains of life. Its role is to catalyze protein synthesis, the messenger RNA (mRNA)-templated formation of amide bonds between α-amino acid monomers. Amide bond formation occurs within a highly conserved region of the large ribosomal subunit known as the peptidyl transferase center (PTC).
In this paper, the authors describe the stepwise design and characterization of a miniaturized PTC, a 284-nucleotide RNA that recapitulates many essential features of the Escherichia coli ribosome. The mini-PTC folds into a native-like tertiary structure under physiological conditions, even in the absence of r-proteins, and engages small molecule analogs of A- and P-site tRNAs. Its sequence differs from the wild type E. coli ribosome at 12 nucleotides that were installed by a cohort of citizen scientists using the online video game Eterna. These base changes improve both secondary structure and tertiary folding as well as the ability to bind small molecule substrate analogs.
This work was a collaboration between the Schepartz lab, the Das lab, and Eterna.
Read the paper: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad1254